Arbeitsgruppe Prof. Dr. Udo Reischl

| Telefon | +49 (0) 941 - 944 6450 | ||||
| Telefax | +49 (0) 941 - 944 6451 | ||||
| udo.reischl@ukr.de | |||||
Themenschwerpunkte
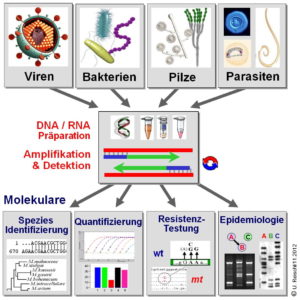
Nukleinsäurediagnostik: Konzeption und Evaluierung von PCR-gestützten Nachweisverfahren zum hochsensitiven, kulturunabhängigen und spezifischen Nachweis von bakteriellen, fungalen und eukaryonten Pathogenen und genetisch determinierten Pathogenitätsfaktoren in klinischem Untersuchungsmaterial. Schwerpunkte sind hier die Optimierung von PCR-gestützten broad range Testsystemen zum Nachweis und zur Differenzierung bakterieller und fungaler Erreger in normalerweise sterilem Probenmaterial, der Aufbau von validierten Sequenzdatenbanken für Speziesmarker zum Design von innovativen Array-Detektionssystemen und einer präzisen Interpretation der Ergebnisse. Optimierung und Etablierung von rationellen Plattformen zur automatisierten Probenaufarbeitung (sample prep) sowie zur PCR-Schnelldiagnostik.
Molekulare Epidemiologie: Etablierung von standardisierten Methoden zur Charakterisierung von molekularen Markern mit deren Hilfe unterschiedliche Isolate einer Spezies unter epidemiologischen Aspekten differenziert werden können. Ziel ist die möglichst schnelle und präzise Analyse von Infektionsketten (online Hygiene).
Das übergeordnete Ziel der Forschungstätigkeit ist die Verfügbarkeit von zuverlässigen same day results für ausgewählte pathogene Erreger bzw. Erregergruppen, um den behandelnden Arzt auch zeitnah mit therapierelevanten Informationen versorgen zu können.
Derzeit sind über 60 Erreger- und Pathogenitätsfaktor-spezifische sowie 12 erregerübergreifende PCR-Testsysteme (größtenteils im LightCycler real-time PCR Format) etabliert und routinemäßig verfügbar. Auf Anfrage werden diese Untersuchungen auch für externe Einsender angeboten.
Vielfältige Aktivitäten zur internen und externen Qualitätssicherung der Molekularen Diagnostik von Infektionserregern.
MITARBEITER
Hier finden Sie den richtigen Ansprechpartner:
UNSERE NEWS
Alle aktuellen News unserer Arbeitsgruppe auf einen Blick:
1a. Reischl, U. (1989) Isolierung und Charakterisierung der Restriktionsenzyme EclXI und McrI. Diplomarbeit am Institut für Biochemie der Ludwig-Maximilians-Universität München.
2. Brensing-Küppers, J., Reischl, U., Schmitz, G., Kaluza, K., Jarsch, M. and Kessler, C. (1990) Mcr I: a novel class-II restriction endonuclease from Micrococcus cryophilus recognizing 5'-CGRY/CG-3'. FEBS 264, 218-222.
3. Rüger, R., Höltke, H.-J., Reischl, U., Sagner, G. and Kessler, C. (1990) Use of the polymerase chain reaction for non-radioactive labeling specific DNA sequences with Digoxigenin. J. Clin. Chem. Clin. Biochem. 28, 566-568.
4. Rüger, R., Höltke, H.-J., Reischl, U., Sagner, G. and Kessler, C. (1991) Use of polymerase chain reaction for non-radioactive labeling of specific DNA sequences with Digoxigenin. BTF 5, Advances Mol. Gen. 3, 277-280.
5. Rüger, R., Höltke, H.-J., Reischl, U., Sagner, G. and Kessler, C. (1991) Labeling of specific DNA sequences with digoxigenin during polymerase chain reaction. In: PCR-TOPICS (Rolfs, A., Schumacher, C., Marx, P. Edts.), Springer Verlag Berlin, 56-58.
6. Reischl, U. (1992) Entwicklung alternativer Techniken zur in vitro Vermehrung von Nukleinsäuren auf der Basis natürlicher Replikations- und Transkriptionsmechansimen. Dissertation zur Erlangung des Doktorgrades der Fakultät für Chemie und Pharmazie der Ludwig-Maximilians-Universität München.
7. Reischl, U., Rüger, R., Kaletta, C., Kessler, C. and Kleiber, J. (1992) Verfahren zur spezifischen Vervielfältigung von Nukleinsäuresequenzen. Europäische Patentanmeldung EP 0545010 A1.
8. Reischl, U., Rüger, R., C., Kessler and Seibl, R. (1994) Process for the specific production of ribonucleic acids. United States Patent US 5,369,003.
9. Reischl, U., Rüger, R., Kessler, C. and Seibl, R. (1992) Verfahren zur spezifischen Herstellung von Ribonukleinsäuren. Europäische Patentanmeldung EP 0534345 A2, Deutsche Patentanmeldung DE 4132133 A1.
10. Reischl, U., Rüger, R. and Kessler, C. (1993) Nonradioactive labeling of polymerase chain reaction products, in: Methods in Molecular Biology, Vol. 15., PCR Protocols: Current Methods and Applications (White, B.A. edt.), Humana Press Inc., Totowa, NJ, pp. 51-62.
11. Wagner, R., Mayer, J., Reischl, U. and Wolf, H. (1993) Möglichkeiten und Ziele der HIV-Diagnostik. mta 8, 675-682.
12. Mayer, J., Reischl, U., v. Poblotzki, A., Hottenträger, B. and Wolf, H. (1994) Neue Virusinfektionen - Hepatitis C, Parvovirus-Infektion und Infektionen mit dem Humanen Herpesvirus 6 (HHV6). mta 9, 529-533.
13. Reischl, U., Mayer, J., Wagner, R. and Wolf, H. (1994) Molekularbiologische Techniken in der medizinischen Diagnostik. mta 9, 612-616 (Teil 1); mta 9, 699-704 (Teil 2).
14. Reischl, U. and Mayer, J. (1993) Moderne Methoden der Nukleinsäure-Diagnostik. Lab. med. 17, 456-464.
15. Mayer, J., Reischl, U., Schwarzmann, F. and Wolf, H. (1993) Pathobiology of Epstein-Barr virus and related diseases. Biotest Bulletin 5, 3-12.
16. Reischl, U. and Hell, W. (1994) DNA-Sequenzierung. In: PCR im medizinischen und biologischen Labor, -Handbuch für den Praktiker- (Wink, M., Wehrle, H. edts.), GIT Verlag, Darmstadt, 41-74.
17. Reischl, U., Rüger, R. and Kessler, C. (1994) Nonradioactive labeling and high-sensitive detection of PCR products. Molecular Biotechnology 1, 229-240.
18. Schwarzmann, F., Wagner, R., Mayer, J., Reischl, U. and Wolf, H. (1993) Aktuelle Perspektiven in der molekularen Virologie. Immun. Infekt. 21, 159-164.
19. Mayer, J., Reischl, U. and Jilg, W. (1994) Klinische Bedeutung der Polymerase-Kettenreaktion in der Infektiologie. Dtsch. med. Wschr. DMW 119, 1625-1629.
20. Reischl, U. and Huber, J. (1994) Einsatz von Fluoreszenzmarkierungen in der automatisierten DNA-Analyse. BIOforum 17 (4/94), 108-111 (Teil 1) und 18 (5/94), 13-17 (Teil 2).
21. Reischl, U., Mayer, J. and Wagner, R. (1993) Aktuelle Methoden der HIV-Diagnostik. BIOforum 16 (12/93), 455-460 (Teil 1) und 17 (1/94), 13-17 (Teil 2).
22. Wagner, R., Mayer, J. and Reischl, U. (1995) Labordiagnostik der HIV-Infektion. Fortschr. Med. 113, 39-45.
23. Mayer, J., Reischl, U. and Wagner, R. (1994) Labordiagnostik der HIV-Infektion. LaborMedizin 17 (1/94), 12-17.
23a. Mayer, J., Reischl, U. and Wagner, R. (1994) Laboratoryina diagnostyka infekcij HIV. GIT specjalnie polska (1/95), 47-52.
24. Reischl, U., Pulz, M., Ehret, W. and Wolf, H. (1994) PCR-based detection of mycobacteria in sputum samples using a simple and reliable DNA extraction protocol. BioTechniques 17, 844-846.
24a. Reischl, U., Pulz, M., Ehret, W. and Wolf, H. (1995) PCR-based detection of mycobacteria in sputum samples using a simple and reliable DNA extraction protocol. BioTechniques Euro Edition Jan/Feb, 24-26.
25. Reischl, U., Leschonsky, B., Hengerer, A. and Kochanowski, B. (1994) Entwicklung serologischer Nachweisverfahren auf Basis von rekombinanten Proteinen. BIOforum 17 (11/94), 454-456 (Teil 1) und 17 (12/94), 506-509 (Teil 2).
26. Meyer, T., Reischl, U., Wolf, H., Schüller, C. and Arndt, R. (1994) Identification of active cytomegalovirus infection by analysis of immediate-early, early and late transcripts in peripheral blood cells of immunodeficient patients. Mol. Cell. Probes 8, 261-271.
27. Wolf, H., Reischl, U. and Motz, M. (1993) Epstein-Barr virus DNA sequences encoding a diagnostically relevant virus capsid antigen, expression clones derived through polymerase chain reaction and the use of this recombinant antigen in diagnostic tests (p23). Europäische Patentanmeldung, and United States Patent US 5,741,656.
28. Reischl, U., Siemon, G., Wolf, H., Ehret, W. and Pulz, M. (1994) PCR-based detection of Mycobacterium tuberculosis in sputum samples using a simple and reliable DNA extraction protocol. Experientia 50, 797 .
29. Reischl, U., Gerdes, C., Motz. M. and Wolf, H. (1996) Expression and purification of an Epstein-Barr virus encoded 23-kDa protein and characterization of its immunological properties. J. Virol. Meth. 57, 71-85.
30. Wagner, R. and Reischl, U. (1994) Neue virologische und immunologische Aspekte der HIV-Infektion, in: HIV-Medizin: Möglichkeiten der individualisierten Therapie. Wissenschaftliche Ergebnisse in der Mitte der 90er Jahre (Jäger, H. edt.), ecomed Verlag, Landsberg/Lech, pp. 31-38.
31. Reischl, U., Kessler, C. and Rüger R. (1994) Novel transcription properties of bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase implying absolute template specifity in discontinuous, nicked, gapped and even mismatched template structures. Nucl. Acids Res., in preparation
32. Prang, N., Reischl, U., Arndt, R., Meyer, T., Mayer, J., Schwarzmann, F. and Wolf, H. (1994) Identification of Epstein-Barr virus transactivator BZLF1 mRNA in uncultured peripheral blood lymphocytes by RT-polymerase chain reaction. Experientia 50, 769.
33. Reischl, U., Hengerer, A., Ehret, W. and Wolf, H. (1994) Ein 29 kD großes Membranprotein von Legionella pneumophila sowie dessen Nukleinsäuresequenz und die Verwendung in Diagnostik und Therapie. Deutsche Patentanmeldung, DE 4419294 A1.
34. Reischl, U. (1994) HIV-Diagnostik - Eine kurze Übersicht der gängigen Nachweisverfahren. Management & Krankenhaus 11, 42-44.
35. Reischl, U. and Kochanowski, B. (1995) Quantitative PCR - A survey of the present technology. Molecular Biotechnology 3, 55-71.
36. Meyer, T., Arndt, R., Stockfleth, E., Flammann, H.T., Wolf, H. and Reischl, U. (1995) Strategy for typing human papillomaviruses by RFLP analysis of PCR products and subsequent hybridization with a generic probe. BioTechniques 19, 632-639.
37. Reischl, U., Pulz, M., Ehret, W. and Wolf, H. (1995) Neue einfache Methode zur DNA-Extraktion aus Mykobakterien. Klin. Lab. 6/95, 493-494.
38. Wagner, R. and Reischl, U. (1995) Neue virologische und immunologische Aspekte der HIV-Infektion. Arzt und Krankenhaus 7, 203-209.
39. Reischl, U. (1995) Recent developments in molecular biology-based clinical diagnosis. Med. Focus Intern. 8, 44-49.
40. Reischl, U. and Naumann, L. (1996) Molekularbiologische Methoden zum Nachweis von Mykobakterien. Fortschr. Med. 114, 237-241.
41. Schröder, K.-H., Naumann, L., Kroppenstedt, R.M. and Reischl, U. (1997) Mycobacterium hassiacum sp. nov., a new rapidly growing thermophilic Mycobacterium. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 47, 86-91.
42. Meyer, T., Arndt, R., Stockfleth, E., Flammann, H.T., Wolf, H. and Reischl, U. (1996) HPV-Typisierung durch RFLP / Hybridisierungsanalyse von PCR-Produkten. BioForum 19, 428-433.
43. Reischl, U. and Gerdes, C. (1996) Preparative SDS PAGE electrophoresis of a recombinant Epstein-Barr virus encoded protein and its application in serodiagnostic test systems. Bio-Rad Application Bulletin 2024.
44. Leschonsky, B., Wolf, H. and Reischl U. (1996) Verwendung des Pinpoint-Expressionssystems zur Herstellung monobiotinylierter rekombinanter Antigene, Boehringer Ingelheim News 7, 1-6.
45. Meyer, T., Scholz, D., Warnecke, G., Kunz, M., Arndt, R., Reischl, U., Wolf, H. and Lissner, R. (1996) Importance of simultaneous cytomegalovirus and Epstein-Barr virus infection in renal transplantation. Clinical and Diagnostic Virology 6, 79-91.
46. v. Poblotzki, A., Gerdes, C., Reischl, U., Wolf, H. and Modrow, S. (1996) Lymphoproliferative responses after infection with human Parvovirus B19. J. Virol. 70, 7327-7330.
47. Jäger, M., Prang, N., Mitterer, M., Larcher, C., Huemer, H.P., Reischl, U., Wolf, H. and Schwarzmann, F. (1996) Pathogenesis of chronic Epstein-Barr virus infection: detection of a virus strain with a high rate of lytic replication. Brit. J. Haematol., 95, 626-636.
48. Reischl, U. and Naumann, L. (1996) Organisation der Laboratoriumsdiagnostik von Infektionskrankheiten - "outsourcing" versus "in house". Arab Medico, 14, 112-116.
49. Reischl, U. (1996) Application of molecular biology-based methods to the diagnosis of infectious diseases. Frontiers in Bioscience, 1, 72-77.
50. Haedicke, W., Wolf, H., Ehret, W. and Reischl, U. (1996) Specific and sensitive two-step polymerase chain reaction assay for the detection of Salmonella species. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis., 15, 603-606.
51. Wagner, R. and Reischl, U. (1996) Qualitativer und quantitativer Nukleinsäurenachweis in der Molekularen Diagnostik von Infektionskrankheiten. In: Virus load und AIDS – Bedeutung der Virusbelastung für die Therapie der HIV Infektion (Jäger, H. edt.), Thieme Verlag, Stuttgart, ISBN 3-13-107716-1, 48-59.
52. Reischl, U., Haber, B., Vandezande, W., De Baere, T. and Vaneechoutte, M. (1997) Long term storage of complete PCR reaction mixtures. BioTechniques, 23, 580-584.
53. Lohmann, C.P., Patmore, A., O'Brart, D., Reischl, U., Winkler von Mohrenfels, C. and Marshall, J. (1997) Regression and wound healing after excimer laser PRK: a histopathological study on human corneas. Eur. J. Ophthalmol., 7, 130-138.
54. Lohmann, C.P., Linde, H.-J., and Reischl, U. (1997) Die Schnelldiagnostik einer infektiösen Endophtalmitis mittels Polymerase-Kettenreaktion (PCR): Eine Alternative zu den konventionellen mikrobiologischen Diagnostikverfahren. Klin. Monatsbl. Augenheilkd., 211, 22-27.
55. Lohmann, C.P., Patmore, A., Reischl, U. and Marshall, J. (1996) The importance of the corneal epithelium in excimer-laser photorefractive keratectomy. German J. Ophthalmol., 5, 368-372.
56. Naumann, L., Jäger, H., Lang, E., Lehn, N., Linde, H.-J., Oros, H., Pausch, G., Poppinger, J., Schwarz, A., Vilsmeier, S. and Reischl, U. (1997) Evaluation of MB Redox - Comparison of a new liquid medium with solid media and the Bactec 460 TB. J. Lab. Med. 21, 31-34.
57. Naumann, L., N. Lehn, H. Wolf and U. Reischl (1997) Neue schnelle kulturelle Nachweismethoden im Mykobakterienlabor. Mikrobiologe, 7, 123-125.
58. Reischl, U. and L. Naumann (1997) Laboratory diagnosis of infectious diseases - outsourcing versus in-house. Medical Focus International 1/1997, 18-23.
59. Lohmann, C.P. and U. Reischl (1997) Rapid diagnosis of infectious endophthalmitis by polymerase chain reaction (PCR): an improvement to conventional microbiological tests ?. SOE '97 - Proceedings of the XIth Congress of the European Society of Ophthalmology (peer reviewed), Monduzzi Editore, Bologna, Italy, pp.709-712.
60. L. Naumann, J. Kaustova, Z. Horak, S. Emler, R. Kroppenstedt and U. Reischl (1997) Mycobacterium bohemicum sp. nov. Spanish Journal of Chemotherapy (Quimotherapia), 10, 56-57.
61. L. Naumann, G. Schonard, M. Havelkova, K.H. Schröder, H. Wolf, N. Lehn and U. Reischl (1997) RFLP-testing for the detection of simultaneous MTB infections. Spanish Journal of Chemotherapy (Quimotherapia), 10, 78.
62. T. Korman, M. Globan, A. Sievers, S. Emler, L. Naumann, H. Wolf, J. Williams, D. Leslie and U. Reischl (1997) A novel Mycobacterium isolated from a man with AIDS. Spanish Journal of Chemotherapy (Quimotherapia), 10, 153.
63. U. Reischl, K. Feldmann, L. Naumann, B. Hirschel and S. Emler (1997) 16S rRNA sequence diversity in Mycobacterium celatum strains caused by two different copies of the 16S rDNA. Spanish Journal of Chemotherapy (Quimotherapia), 10, 174.
64. Reischl, U., N. Lehn, H. Wolf, and L. Naumann (1997) Clinical evaluation of the automated COBAS Amplicor MTB assay at respiratory and nonrespiratory specimens (Abstract). J. Microbiol. Meth. 30, 235-253.
65. Reischl, U., and C.P. Lohmann (1997) Die Polymerase-Kettenreaktion (PCR) und ihre Anwendungsmöglichkeiten zur infektiologischen Diagnsotik in der Opthalmologie. Klin. Monatsbl. Augenheilkd. 211, 227-234.
66. Lohmann, C.P., E. Hoffmann, and U. Reischl (1998) Epidermal growth factor (EGF) in tears in excimer laser photorefractive keratectomy. Responsible for postoperative refraction and "haze"? Ophthalmologe 95, 80-87.
67. Lohmann, C.P., M. Heep, H.-J. Linde, and U. Reischl (1998) Listeria monocytogenes-induzierte Endophthalmitis bei einem sonst gesunden Individuum: PCR-gestützte Schnelldiagnostik als Grundlage für eine erfolgreiche Therapie. Klin. Monatsbl. Augenheilkd. 212, 55-58.
68. Hengerer, A., E. Prohaska, J. Decker, S. Hauck, E. Yacoub, C. Kösslinger, U. Reischl, S. Drost, and H. Wolf (1998) Bioactive films. Materials Science Forum 288, 169-178.
69. Reischl, U., C. Gerdes and I.P. Thrippleton (1998) Screening for recombinant E.coli using antibiotic test strips. BioTechniques 24, 550-553.
70. Reischl, U. (1998) PCR-based cloning and subsequent expression of antigenic proteins in Escherichia coli. In: Molecular Diagnosis of Infectious Diseases (Reischl, U. edt.), Humana Press Inc., Totowa, NJ, pp. 157-169.
71. Reischl, U. (1998) Purification and immunological characterization of recombinant antigens expressed in the form of insoluble aggregates (inclusion bodies). In: Molecular Diagnosis of Infectious Diseases (Reischl, U. edt.), Humana Press Inc., Totowa, NJ, pp. 331-345.
72. Appleby, P. and U. Reischl (1998) Monoclonal antibody-based immunoassays. In: Molecular Diagnosis of Infectious Diseases (Reischl, U. edt.), Humana Press Inc., Totowa, NJ, pp. 487-502.
73. Reischl, U. (1998) Respiratory and nonrespiratory specimen evaluation with COBAS Amplicor MTB. Roche Benchmark 4, 10-11.
74. Reischl, U. and B. Haber (1998) Preparation of PCR templates from primary fecal cultures for the detection of Escherichia coli Shiga-like toxin genes. In: Nucleic Acid Isolation and Purification Manual, Boehringer Mannheim, pp. 24-26.
75. Weber, A., U. Reischl, and L. Naumann (1998) Isolation of Mycobacterium africanum from a bull in Northern Bavaria. Berl. Münch. Tierärztl. Wochenschr. 111, 6-8.
76. Tortoli, E., U. Reischl, G. Besozzi, and S. Emler (1998) Characterization of an isolate belonging to the newly described species Mycobacterium hassiacum. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 30, 193-196.
77. Reischl, U., K. Feldmann, L. Naumann, B.J.M. Gaugler, B. Ninet, B. Hirschel, and S. Emler (1998) 16S rRNA sequence diversity in Mycobacterium celatum strains caused by the presence of two different copies of 16S rRNA gene. J. Clin. Microbiol. 36, 1761-1764.
78. Neubauer, H., U. Reischl, S. Ropp, J.J. Esposito, H. Wolf, and H. Meyer (1998) Specific detection of monkeypox virus by polymerase chain reaction. J. Virol. Methods 74, 201-207.
79. Körpert, S., U. Reischl, T. Meyer, C.N. Wang, and T. Steinmüller (1998) Einsatz der AmpliSensor Technologie zur Detektion von Borrelia burgdorferi 'sensu lato'. Hygiene und Mikrobiologie 2/98, 50-51.
80. Reischl, U., B. Haber, H. Melzl, L. Naumann, N. Lehn, H. Wolf, S. Emler, and A.G. Nerlich (1998) Molecular evidence of tuberculosis in an ancient Egyptian mummy. Hygiene und Mikrobiologie 2/98, 54-55.
81. Schröder, H.D., C. Ludwig, W. Jakob, U. Reischl, M. Stolte, and N. Lehn (1998) Chronic gastritis in tigers associated with Helicobacter acinonyx. J. Comp. Pathol. 119, 67-73.
82. Reischl, U., S. Emler, Z. Horak, J. Kaustova, R.M. Kroppenstedt, N. Lehn, and L. Naumann (1998) Mycobacterium bohemicum sp. nov., a new slow-growing scotochromogenic mycobacterium. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 48, 1349-1355.
83. Reischl, U., and H. Wolf (1998) The use of molecular methods in infectious diseases. Biotest Bulletin, 6, 3-20.
84. Lohmann, C.P., M. Heep, H.J. Linde, V.P. Gabel, and U. Reischl (1998) Diagnosis of infectious endophthalmitis after cataract surgery by polymerase chain reaction. J. Cataract. Refract. Surg. 24, 821-826.
85. Schroeder, J., U. Reischl, and B. Lorenz (1998) Ultrastructural and PCR evidence of Spiroplasma spp. in human cataract eye lens. Electron. Microscopy 4, 669-670.
86. Reischl, U., N. Lehn, H. Wolf, and L. Nauman (1998) Clinical evaluation of the automated COBAS Amplicor MTB assay for testing respiratory and non-respiratory specimens. J. Clin. Microbiol. 36, 2853-2860.
87. Samra, Z., L. Kaufmann, S. Ashkenazi, A. Zeharia, J. Amir, J. Bahar, U. Reischl, and L. Naumann (1999) Optimal detection and identification of Mycobacterium haemophilum from pediatric patients with cervical lymphadenopathy. J. Clin. Microbiol. 37, 832-835.
88. Reischl, U., L. Naumann, M. Hengstler, A.-M. Fahr, K. Feldmann, and S. Rüsch-Gerdes (1999) Clinical Evaluation of the ABBOTT LCx MTB assay for testing respiratory and nonrespiratory specimens. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 5, 98-100.
89. Lohmann, C.P., V.-P. Gabel, M. Heep, H.-J. Linde, and U. Reischl (1998) Listeria monocytogenes-induced endogenous endophthalmitis in an otherwise healthy individual: rapid PCR-diagnosis as the basis for effective treatment. Eur. J. Ophthalmol. 9, 53-57.
90. Reischl, U. (1998) Nukleinsäure-Diagnostik zum Nachweis und zur Differenzierung von Mykobakterien. In: "Tuberkulose Aktuell - Neue Aspekte zur Epidemiologie, Diagnostik, Therapie und Resistenzsituation" (Sandberger, G. edt.), Grünenthal GmbH, pp. 9-17.
91. Lohmann, C.P., U. Reischl, H.-J. Linde, and V.-P. Gabel (1999) Improved detection of microorganisms in endopthalmitis by polymerase chain reaction. Retina, UVEA Issue, 222-228.
92. Zink, A., C.J. Haas, E. Molnár, U. Szeimies, U. Reischl, A. Marcsik, Y. Ardagna, O. Dutour, G. Pálfi, and A.G. Nerlich (1999) Identification of Mycobacterium tuberculosis in different stages of tuberculosis in ancient bone samples from Hungary. J. Paleopathol. 11, 126.
93. Zink, A., U. Reischl, H. Wolf, and A.G. Nerlich (1999) Molecular analysis of DNA in Egyptian mummy material for the identification of pathogenic bacteria. Paleopathology Newsletter 106, 10.
94. Neubauer H., U. Reischl, J. Köstler, S. Aleksic, E.-J. Fincke, and H. Meyer (1999) Variations in the 16S rRNA gene sequence of Yersinia enterocolitica influence the specificity of molecular identification systems. Zent. bl. Bakteriol. 289, 329-337.
95. Reischl, U., and B. Kochanowski (1999) Quantitative PCR: a survey of the present technology. In: Quantitative PCR Protocols (Kochanowski, B., and Reischl, U., eds.), Humana Press Inc., Totowa, NJ, pp. 3-30.
96. Daeschlein, G., E. Kiefer, F. Portaels, R. Kroppenstedt, L. Naumann, U. Reischl, H. Eckert, and R. Lange (1998) Pulmonary infiltrative infection with a new atypical Mycobacterium complicating pulmonary sarcoidosis. Rev. Portug. Pneumologia 4, 352-357.
97. Zink, A., Ch. Haas, U. Reischl, H. Wolf, and A.G. Nerlich (1999) Identification of Mycobacterium tubercuosis in bone and soft tissue samples from ancient Egyptian mummies. In: Research '99. (D. Teupser, G. Enders, Th. Demant, D. Seidel, edt.), MMW Taschenbuch, Urban & Vogel Medizinischer Verlag, München, pp. 452-455.
98. Schwarzmann, F., R. von Baehr, M. Jäger, N. Prang, S. Böhm, U. Reischl, H. Wolf, and W.P. Bieger (1999) A case of severe chronic active infection with Epstein-Barr virus: immunologic deficiencies associated with a lytic virus strain. Clin. Infect. Dis. 29, 626-631.
99. Reischl, U., and B. Leppmeier (1999) Simultaneous detection of Staphylococcus aureus and methicillin resistance gene-specific markers using the multi color option. LightCycler System manual. Roche Molecular Biochemicals, Mannheim, pp. 18-20.
100. Lohmann, C., E. Hoffmann, and U. Reischl (1999) The effects of epidermal growth factor in the tear fluid on postoperative refraction and haze after photorefractive keratectomy. Lasers and Light in Ophthalmology. 9, 5-14.
101. Zink, A., U. Reischl, H. Wolf, A.G. Nerlich, and R. Miller (2001) Corynebacterium in ancient Egypt. Medical History, 45, 267-272.
102. Reischl, U., and L. Naumann (2000). Tradition und Hightech in der Tuberkulosediagnostik. Roche Dialog 1, 6-9.
103. Reischl, U., and L. Naumann (2000). Labordiagnostischer Nachweis von atypischen Mykobakterien. Roche Dialog 1, 10-13.
104. Roth, A., U. Reischl, A. Streubel, L. Naumann, R.M. Kroppenstedt, M. Habicht, M. Fischer, and H. Mauch (2000) Novel diagnostic algorithm for identification of mycobacteria using genus-specific amplification of the 16S-23S rRNA gene spacer and restriction endonucleases. J. Clin. Microbiol. 38, 1094-1104.
105. Lohmann, C.P., and U. Reischl (2000) PCR – Valuable diagnostic tool for identifying pathogens causing endophthalmitis. EuroTimes, January issue, pp.34-35.
106. Reischl, U., H. Blenk, H.J. Boltze, L. Drath, B. Ganster, H. Geiss, U. Göbel, G. Haase, K. Janitschke, R. Küchler, W. Mathys, T. Mertens, C. Schoerner, and S. Ziesig (2000) Checkliste Mikrobiologie und Hygiene – Molekularbiologie in der Infektionsdiagnostik. In: Handbuch für die Akkreditierung Medizinischer Laboratorien (AML und ZLG, Hrsg.). Bernd-Michael Paschke Verlag, Berlin, ISBN 3-929711-11-X, pp. 121-136.
107. Reischl, U., H.J. Linde, M. Metz, B. Leppmeier, and N. Lehn (2000) Rapid identification of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus and simultaneous species confirmation using real-time fluorescence. J. Clin. Microbiol. 38, 2429-2433.
108. Lohmann, C.P., H.J. Linde, and U. Reischl (2000) Improved detection of microorganisms by polymerase chain reaction in delayed endophthalmitis after cataract surgery. Ophthalmology 107, 1047-1052.
109. Leppmeier, B., and U. Reischl (2000) Nucleic acid purification - method for the isolation of mycobacterial DNA. Roche Molecular Biochemicals Application Note No. HP 2, ISSN 1436-1191.
110. Reischl, U. (2000) LightCycler PCR protocols in clinical bacteriology. School of Medicine Proceedings in Molecular Diagnostics, Vol. 4, Nagoya University, Japan, pp. 31-45.
111. Reischl, U., B. Leppmeier, C. DaCosta, T. Miethke, and N. Lehn (2000) Comparison of MagNAPure LC, High Pure PCR Template Preparation Kit, and phenol/choloroform for the extraction of total genomic DNA from C. pneumoniae-infected Hep-2 cells. Biochemica 3, 9-12.
112. Lohmann, C.P., C. Winkler v. Mohrenfels, B. Gabler, U. Reischl, and B. Kochanowski (2000) Die Polymerase-Kettenreaktion (PCR) zur mikrobiologischen Diagnostik einer persistierenden infektiösen Keratitis: Eine klinische Studie bei 16 Patienten. Klin. Monatsbl. Augenheilkd. 217, 37-42.
113. Reischl, U. (2000) Bacterial identification by broad-range PCR and DNA microarray technology. Medizinische Genetik 12, 309-311.
114. Hartmann, K., K. Gerle, J. Hirschberger, U. Reischl, and W. Hermanns (2000) Lungentuberkulose bei einer Katze. Tierärztl. Prax. 28, 197-202.
115. Haas C.J., A. Zink, E. Molnar, U. Szeimies, U. Reischl, A. Marcsik, Y. Ardagna, O. Dutour, G. Palfi, and A.G. Nerlich (2000) Molecular evidence for different stages of tuberculosis in ancient bone samples from Hungary. Am. J. Phys. Anthropol. 113, 293-304.
116. Lohmann, C.P., B. Gabler, G. Kroher, D. Spiegel, H.J. Linde, and U. Reischl (2000) Disciforme keratitis caused by Bartonella henselae: an unusual ocluar complication in cat scratch disease. Eur. J. Ophthalmol. 10, 257-258.
117. Lohmann, C.P., U. Reischl, and J.J. Marshall (1999) Regression and epithelial hyperplasia after myopic photorefractive keratectomy in a human cornea. Cataract. Refract. Surg. 25, 712-715.
118. Zink, A., U. Reischl, C. Haas, H. Wolf, and A.G. Nerlich (2000) Molecular identification of Mycobacterium tuberculosis in ancient human remains. Biol. Chem. 381, S228.
119. Roth, A., U. Reischl, N. Schönfeld, L. Naumann, S. Emler, M. Fischer, H. Mauch, R. Loddenkemper, and R.M. Kroppenstedt (2000) Mycobacterium heckeshornense sp. nov., a new pathogenic slowly growing Mycobacterium sp. causing cavitary lung disease in an immunocompetent patient. J. Clin. Microbiol. 38, 4102-4107.
120. Zink, A., U. Reischl, H. Wolf, and A.G. Nerlich (2000). Molecular evidence for bacteremia by gastrointestinal pathogenic bacteria in an infant mummy from ancient egypt. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 124, 1614-1618.
121. Gabler, B., H.-J. Linde, U. Reischl, and C.P. Lohmann (2000) Disciforme keratitis after Bartonella henselae-associated cat scratch disease: a rare ocular complication. Klin. Monatsbl. Augenheilkd. 217, 299-302.
122. Noppen, C., I. Martinato, U. Reischl, and C. Schäfer (2001) High-speed purification and detection of Bordetella pertussis – a straightforward application of the MagNA Pure LC and the LightCycler system in microbiological research. Biochemica 1, 17-20.
123. Reischl, U., S. Burggraf, B. Leppmeier, H.-J. Linde, and N. Lehn (2001) Rapid and specific detection of Bordetella pertussis in clinical specimens by LightCycler PCR. In: Rapid Cycle Real-Time PCR: Methods and Applications (Meurer, S., Wittwer, C., and Nakagawra, K.-I., eds.), ISBN 3-540-66736-9, Springer Press, Heidelberg, pp. 313-322.
124. Reischl, U., B. Leppmeier, M. Heep, D. Beck, and N. Lehn (2001) Rapid and specific detection of Helicobacter pylori by LightCycler PCR. In: Rapid Cycle Real-Time PCR: Methods and Applications (Meurer, S., Wittwer, C., and Nakagawra, K.-I., eds.), ISBN 3-540-66736-9, Springer Press, Heidelberg, pp. 323-330.
125. Linde, H.-J., M. Schmidt, E. Fuchs, U. Reischl, H.-H. Niller, and N. Lehn (2001) In vitro activities of six Quinolones and mechanisms of resistance in Staphylococcus aureus and coagulase-negative Staphylococci. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 45, 1553-1557.
126. Reischl, U., N. Lehn, G.N. Sanden, and M. Löffelholz (2001) Real-time PCR assay targeting IS481 of Bordetella pertussis and molecular basis for detecting Bordetella holmesii. J. Clin. Microbiol. 39, 1963-1966.
127. Zink A., C.J. Haas, U. Szeimies, U. Reischl, and A.G. Nerlich (2001) Molecular analysis of skeletal tuberculosis in an ancient Egyptian population. J. Med. Microbiol. 50, 355-366.
128. Reischl, U., K. Kösters, B. Leppmeier, H.-J. Linde, and N. Lehn (2001) Rapid detection and simultaneous differentiation of Bordetella pertussis and Bordetella parapertussis in clinical specimens by LightCycler PCR. In: Rapid Cycle Real-Time PCR: Methods and Applications (Reischl, U., Wittwer, C., and Cockerill, F., eds.), ISBN 3-540-41881-4, Springer Press, Heidelberg, pp. 31-44.
129. Reischl, U., H.-J. Linde, B. Leppmeier, and N. Lehn (2001) Duplex LightCycler PCR assay for the rapid detection of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus and simultaneous species confirmation. In: Rapid Cycle Real-Time PCR: Methods and Applications (Reischl, U., Wittwer, C., and Cockerill, F., eds.), ISBN 3-540-41881-4, Springer Press, Heidelberg, pp. 93-108.
130. Reischl, U., E. Samoilovich, V. Kolodkina, N. Lehn, and H.-J. Linde (2001) Rapid detection of toxigenic Corynebacterium diphtheriae by LightCycler PCR. In: Rapid Cycle Real-Time PCR: Methods and Applications (Reischl, U., Wittwer, C., and Cockerill, F., eds.), ISBN 3-540-41881-4, Springer Press, Heidelberg, pp. 71-82.
131. Noppen, C., U. Reischl, and C. Schäfer (2001) Rapid, automated sample processing and detection of numerous bacteria using the MagNA Pure LC and the LightCycler system. Biochemica 3, 11-14.
132. Leppmeier, B., and U. Reischl (2001) Einsatz der PCR zum Nachweis und zur Differenzierung von Mykobakterien. MTA Dialog 8, 674-679.
133. Wood, H., U. Reischl, and R. Peeling (2001) Rapid detection and quantification of Chlamydia trachomatis in clinical specimens by LightCycler PCR. In: Rapid Cycle Real-Time PCR: Methods and Applications (Reischl, U., Wittwer, C., and Cockerill, F., eds.), ISBN 3-540-41881-4, Springer Press, Heidelberg, pp. 115-132.
134. Tortoli, E., C. Piersimoni, R.M. Kroppenstedt, J.I. Montoya-Burgos, U. Reischl, A. Giacometti, and S. Emler (2001) Mycobacterium doricum sp. nov. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 51, 2007-2012.
135. Lohmann, C.P., C. Winkler von Mohrenfels, U. Reischl, A. Muller, and J.L. Guell (2001) Screening of myopic LASIK patients with increased wound healing – quantifying epidermal growth factor mRNA in corneal epithelial cells. Ophtahlmologe 98, 460-465.
136. Kirchgesser, M., M. B. Alberdi, M. Bollwein, B. Miedl, W. Malmberg, and U. Reischl (2001) MagNAPure LC DNA isolation kit III (bacteria, fungi) – Automated isolation of bacterial DNA from various clinical sample materials. Biochemica 4, 4-7.
137. Meerbach, A., B. Gruhn, R. Egerer, U. Reischl, F. Zintl, and P. Wutzler (2001) Semiquantitative PCR analysis of Epstein-Barr virus DNA in clinical samples of patients with EBV-associated diseases. J. Med. Virol. 65, 348-357.
138. Mayer, J., A. Schmitt, E.-B. Bröcker, and U. Reischl (2001) Rapid Cycle Real-Time PCR for early diagnosis of infections due to Trichophyton verrucosum. Mycoses 44: 212-213.
139. Wellinghausen, N., O. Landt, and U. Reischl (2001) Rapid detection and simultaneous differentiation of Legionella spp. and Legionella pneumophila in potable water samples and respiratory specimens by LightCycler PCR. In: Rapid Cycle Real-Time PCR: Methods and Applications (Reischl, U., Wittwer, C., and Cockerill, F., eds.), ISBN 3-540-41881-4, Springer Press, Heidelberg, pp. 45-58.
140. Bialek, R., M. Weiss, K. Bekure-Nemariam, L.K. Najvar, M.B. Alberdi, J.R. Graybill, and U. Reischl (2002) Detection of Cryptococcus neoformans DNA in tissue samples by nested and real-time PCR assays. Clin. Diagn. Lab. Immunol. 9:461-469.
141. Reischl, U., M.T. Youssef, J. Kilwinski, N. Lehn, W.L. Zhang, H.Karch, and N.A. Strockbine (2002). Real-time fluorescence PCR assays for the detection and characterization of Shiga toxin, intimin and enterohemolysin genes from Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli. J. Clin. Microbiol. 40:2555-2565.
142. Lorenz, B., J. Schroeder, and U. Reischl (2002) First evidence of an endogenous Spiroplasma sp. infection in humans manifesting as unilateral cataract associated with anterior uveitis in a premature baby. Graefe's Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 240:348-353.
143. Kösters, K., U. Reischl, J. Schmetz, M. Riffelmann, C.-H. Wirsing von König (2002) Real-time LightCycler PCR for detection and discrimination of Bordetella pertussis and Bordetella parapertussis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 40:1719-1722.
144. Linde, H.-J., J. Hahn, E. Holler, U. Reischl, and N. Lehn (2002) Septicemia due to Acinetobacter junii: case report. J. Clin. Microbiol. 40:2696-2697.
145. Reischl, U. and Gerdes, C. (2002) Preparative SDS PAGE electrophoresis of a recombinant Epstein-Barr virus encoded protein and its application in serodiagnostic test systems. Bio-Rad Technical Note 2024.
146. Winkler von Mohrenfels, C., U. Reischl, B. Gabler, and C.P. Lohmann (2002) "Corneal haze" nach photorefraktiver Keratektomie - Einfluß der individuellen Kollagen-Typ-IV Synthese auf die postoperative Hornhauttrübung. Opthalmologe 99:532-537.
147. Zink, A., U. Reischl, H. Wolf, and A. Nerlich (2002) Molecular analysis of ancient microbial infections. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 213:141-147.
148. Winkler von Mohrenfels, C., U. Reischl, and C.P. Lohmann (2002) Corneal haze after photorefractive keratectomy for myopia. Role of collagen IV mRNA typing as a predictor of haze. J. Cataract. Refract. Surg. 28:1446-1451.
149. Reischl, U., H.-J. Linde, N. Lehn, O. Landt, K. Barratt, and N. Wellinghausen (2002). Direct detection and differentiation of Legionella spp. and Legionella pneumophila in clinical specimens by dual-color real-time PCR and melting curve analysis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 40:3814-3817.
150. Reischl, U., N. Lehn, U. Simnacher, R. Marre, and A. Essig (2003) Rapid and standardized detection of Chlamydia pneumoniae using LightCycler real-time fluorescence PCR. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 21:54-57.
151. Bulajic, M., P. Maisonneuve, W. Schneider-Brachert, P. Muller, U. Reischl, B. Stimec, N. Lehn, A.B. Lowenfels, and M. Lohr (2002) Helicobacter pylori and the risk of benign and malignant biliary tract disease. Cancer 95:1946-1953.
152. Mijs, W., K. De Vreese, A. Devos, H. Pottel, A. Valgaeren, C. Evans, J. Norton, D. Parker, L. Rigouts, F. Portaels, U. Reischl, S. Watterson, G. Pfyffer, and R. Rossau (2002) Evaluation of a commercial Line Probe assay for identification of Mycobacterium species from liquid and solid culture. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 21:794-802.
153. Zink, A., C. Sola, U. Reischl, W. Grabner, N. Rastogi, H. Wolf, and A.G. Nerlich (2003) Characterization of Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex findings from Egyptian mummies by spoligotyping. J. Clin. Microbiol. 41:359-367.
154. Cloud, J.L., W.C. Hymas, A. Turlak, A. Croft, U. Reischl, J.A. Daly, and K.C. Carroll (2003) Description of a multiplex Bordetella pertussis and Bordetella parapertussis LightCycler PCR assay with inhibition control. Diagn. Microbol. Infect. Dis. 46:189-195.
> http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0732-8893(03)00045-2
155. Reischl, U., S. Bretagne, D. Krüger, P. Ernault, and J.-M. Costa (2003) Comparison of two DNA targets for the diagnosis of toxoplasmosis by Real-Time PCR using fluorescence resonance energy transfer hybridization probes. BMC Infect. Dis. 3:7.
> http://www.biomedcentral.com/1471-2334/3/7 .
156. Zink, A.R., W. Grabner, U. Reischl, H. Wolf, and A.G. Nerlich (2003) Molecular study on human tuberculosis in three geographically distinct and time delineated populations from ancient Egypt. Epidemiol. Infect. 130:239-249. .
157. Kaustova, J., V. Meissner, U. Reischl, J. Satinska, V. Vincent, and L. Naumann (2003) Pulmonary disease due to Mycobacterium malmoense in the Czech Republic. Stud. Pneumol. Phthiseol. 63, 59-63.
158. Krüger, D., and U. Reischl (2003) Toxoplasmose: Wichtige Ergänzung der Labordiagnostik durch eine quantitative real-time Polymerase-Kettenreaktion (PCR) - Bisherige Erfahrungen und Empfehlungen zu den Indikationen. Epidemiol. Bull. 27:210-211.
159. Sütterlin, K., R. Englert, T. Schmidt-Wieland, J. Schmitt, U. Reischl, and N. Lehn (2003) Sporadic cases of Staphylococcus aureus organisms negative for a species-specific 442-bp chromosomal fragment. J. Clin. Microbiol. 41:3449.
160. Wilson, D.A., B. Yen-Lieberman, U. Reischl, S.M.Gordon, and G.W. Procop (2003) Detection of Legionella pneumophila by Real-Time PCR for the mip Gene. J. Clin. Microbiol. 41:3327-3330. > http://jcm.asm.org/cgi/reprint/41/7/3327.pdf
161. Zielenski, R., T. Sause, C. Kriegbaum, M. Bollwein, U. Reischl, and J. Steinbiss (2003) Purified reagents enable automated DNA extraction for highly sensitive PCR in microbiology. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 9: P522.
162. Reischl, U., N. Lehn, H. Wolf, and E. Straube (2003) "Bakteriengenom-Nachweis PCR / NAT": Eine neue Ringversuchsreihe von INSTAND e.V. zur externen Qualitätskontrolle molekularbiologischer Nachweisverfahren in der bakteriologischen Diagnostik. Mikrobiologe 13:149-156.
163. Michel, H., B. Wilske, G. Hettche, G. Gottner, C. Heimerl, U. Reischl, U. Schulte-Spechtel, and V. Fingerle (2004) An ospA-polymerase chain reaction / restriction fragment length polymorphism-based method for sensitive detection and reliable differentiation of all European Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato species and OspA types. Med. Microbiol. Immunol. 193: 219-226. > http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00430-003-0196-8
164. Kaustova, J., J. Kolcakova, U. Reischl, R. Curik, and L. Naumann (2003) Isolation of Mycobacterium celatum from an AIDS patient. Stud. Pneumol. Phthiseol. 63: 140-144.
165. Reischl, U., H. Wolf, and D. Krüger (2003) Aktueller Stand des Nachweises von Toxoplasma gondii DNA mittels qualitativer und quantitativer PCR. J. Lab. Med. 27: 393-397.
166. Shrestha, N.K., M.J. Tuohy, G.S. Hall, S.M. Gordon, U. Reischl, and G.W. Procop (2003) Detection and differentiation of Mycobacterium tuberculosis from MOTT by LightCycler PCR and melting curve analysis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 41: 5121-5126. [IF=3,56] > http://jcm.asm.org/cgi/reprint/41/11/5121.pdf
167. Bialek, R., J. Kern, T. Hermann, R. Tijerina, L. Cecenas, U. Reischl, and G.M. Gonzalez (2004) PCR assays for identification of Coccidioides posadasii based on the nucleotide sequence of the proline-rich antigen. J. Clin. Microbiol. 42: 778-783. . [IF=3,56] > http://jcm.asm.org/cgi/reprint/42/2/778.pdf
168. Wellinghausen, N., B. Wirths, A.R. Franz, L.Karolyi, R. Marre, and U. Reischl (2004) Algorithm for the identification of bacterial pathogens in positive blood cultures by real-time LightCycler PCR with sequence-specific probes. Diagn. Microbol. Infect. Dis. 48:229-241. . > http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00430-003-0196-8 [IF=1,69]
169. Linde, H.-J., R. Kobuch, S. Jayasinghe, U. Reischl, N. Lehn, S. Kaulfuss and L. Beutin (2004) Vibrio metschnikovii, a rare cause of wound infection. J. Clin. Microbiol. J. Clin. Microbiol. 42:4909-4911. [IF=3,56] http://jcm.asm.org/cgi/reprint/42/10/4909.pdf
170. von Loewenich, F.D., D. Scorpio, U. Reischl, J.S. Dumler and C. Bogdan (2004) Control of Anaplasma phagocytophilum, an obligate intracellular pathogen, in the absence of inducible nitric oxide synthase, phagocyte NADPH oxidase, tumor necrosis factor, toll-like receptor (TLR)2 and TLR4, or the TLR adaptor molecule MyD88. Eur. J. Immunol. 34:1789-1797. > http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/eji.200425250
171. Reischl, U. (2004) Purification and immunological characterization of recombinant antigens expressed in the form of insoluble aggregates (inclusion bodies).
Methods Mol Med. 2004;94:213-224. In: Molecular Diagnosis of Infectious Diseases (Decker, J. and U. Reischl, edt.), Humana Press Inc., Totowa, NJ, pp. 213-224.
172. Reischl, U., N. Lehn, H. Wolf, and E. Straube (2004) "Bakteriengenom-Nachweis PCR / NAT": Eine neue Ringversuchsreihe von INSTAND e.V. zur externen Qualitätskontrolle molekularbiologischer Nachweisverfahren in der bakteriologischen Diagnostik. Hyg. Mikrobiol. 8:19-21.
173. Reischl, U., M.T. Youssef, H. Wolf, E. Hyytia-Trees, and N.A. Strockbine (2004) Real-time fluorescence PCR assays for the detection and characterization of heat-labile I and heat-stable I enterotoxin genes from enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. J. Clin. Microbiol. 42:4092-4100. [IF=3,56] http://jcm.asm.org/cgi/reprint/42/9/4092.pdf
174. Hierl, T., U. Reischl, P. Lang, H. Hebart, M. Stark, P. Kyme, and I.B. Autenrieth (2004) Preliminary evaluation of one conventional nested and two real-time PCR assays for the detection of Toxoplasma gondii in immunocompromised patients. J Med. Microbiol. 53: 629-632. [pdf] [IF=2,48] > http://dx.doi.org/10.1099/jmm.0.45566-0
175. Reischl, U., M.W. Pfaffl, M. Kubista, and C.T. Wittwer (2004) 1st International qPCR symposium & application workshop. Forschung & Diagnostik 4:38-39.
> www-LINK (STRG & Klick)
176. Reischl, U., N. Lehn, H. Wolf, and E. Straube (2004) "Bakteriengenom-Nachweis PCR / NAT": Auswertung des aktuellen Ringversuchs von INSTAND e.V. zur externen Qualitätskontrolle molekularbiologischer Nachweisverfahren in der bakteriologischen Diagnostik. Mikrobiologe 14:106-116.
177. Reischl, U., N. Lehn, H. Wolf, and E. Straube (2004) "Bakteriengenom-Nachweis PCR / NAT": Auswertung des aktuellen Ringversuchs von INSTAND e.V. zur externen Qualitätskontrolle molekularbiologischer Nachweisverfahren in der bakteriologischen Diagnostik. Mikrobiologe 14:183-192.
178. Lehn, N., Schneider-Brachert, W., Kaiser, P., Reischl, U., and H. Linde (2004) Same-day MRSA admission screening by real-time PCR (RT-PCR) directly from the swab. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 42: A106.
179. Wilson, D., B. Yen-Lieberman, U. Reischl, I. Warshawsky, and G.W. Procop (2004) Comparision of five methods for extraction of Legionella pneumophila from respiratory specimens. J. Clin. Microbiol. 42:5913-5916. [IF=3,56]
> http://jcm.asm.org/cgi/reprint/42/12/5913.pdf
180. Burggraf, S., U. Reischl, N. Malik, M. Bollwein, L. Naumann, and B. Olgemöller (2005) An internally controlled, large volume LightCycler assay for detection of Mycobacterium tuberculosis: comparison with the COBAS AMPLICOR assay on clinical samples. J. Clin. Microbiol. 43:1564-1569. [IF=3,56] > http://jcm.asm.org/cgi/reprint/43/4/1564.pdf
181. Poppert, S., A. Essig, B. Stöhr, A. Steingruber, B. Wirths, S. Juretschko, U. Reischl, and N. Wellinghausen (2005) Rapid diagnosis of bacterial meningitis by real-time polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH). J. Clin. Microbiol. 43:3390-3397. [IF=3,56] > http://jcm.asm.org/cgi/reprint/43/7/3390.pdf
182. Schmid, M., G. Wolf, O.-R. Kaaden, U. Reischl, P. Meyer and H. Koop (2005) Seroprävalenz von Leptospiren in bayerischen Rinderherden und Nachweis von Leptospiren in abortiven Feten. Tierärztl. Umschau 60:262-267. [IF= 0,13]
183. Reischl, U., M. Bollwein, M.B. Alberdi, H. Girgnhuber, W. Malmberg, V. Nieswandt, R. Zielenski, and M. Kirchgesser (2005) Automated rapid isolation of bacterial DNA from various samples using the MagNA Pure Compact system. Biochemica 2: 12-15.
184. Linde H.J., F. Wagenlehner, B. Strommenger, I. Drubel, J. Tanzer, U. Reischl, U. Raab, C. Holler, K.G. Naber, W. Witte, F. Hanses, B. Salzberger, and N. Lehn (2005) Healthcare-associated outbreaks and community-acquired infections due to MRSA carrying the Panton-Valentine leucocidin gene in southeastern Germany. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 24:419-422. [IF= 1,74] > http://www.springerlink.com/media/8q66p67752224.pdf
184 a. Linde H.J., F. Wagenlehner, B. Strommenger, I. Drubel, J. Tanzer, U. Reischl, U. Raab, C. Holler, K.G. Naber, H. Wolf, W. Witte, and N. Lehn (2005) "Community-acquired MRSA". Deutsches Ärzteblatt 102:A1070-1071.
http://aerzteblatt.lnsdata.de/pdf/102/15/a1070.pdf
185. Raab, U., D. Kahlau, F. Wagenlehner, U. Reischl, N. Lehn, C. Höller, and H.-J. Linde (2005) Prevalence and risk factors for community-acquired methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus carriage anmong residents and staff of a German nursing home. Infect. Control Hosp. Epidemiol. 27:208-211.
186. Kaustova, J., J.Boznsky, J. Svobodova, J. Wendrinska, P. Zima, R. Zichacek, D. Rosinska, H. Blazkova, D. Chocholac, R. Pacola, D. Velart, J. Palion, U. Reischl, and L. Naumann (2005) Microbiological diagnosis of mycobacterioses caused by Mycobacterium haemophilum. Klin. Mikrobiol. Infekc. Lek. 11:105-108.
187. Uhl, J.R., E.A. Vetter, K.L. Boldt, B.W. Johnston, K.D. Ramin, M.J. Adams, P. Ferrieri, U. Reischl, and F.R. Cockerill 3rd. (2005) Use of the Roche LightCycler Strep B assay for detection of group B Streptococcus from vaginal and rectal swabs. J. Clin. Microbiol. 43:4046-4051. > http://jcm.asm.org/cgi/reprint/43/8/4046.pdf
188. Maier, J., H. Melzl, U. Reischl, I. Drubel, W. Witte, N. Lehn, and H.J. Linde (2005) Panton-Valentine leukocidin-positive methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in Germany associated with travel or foreign family origin. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 24:637-639. > http://www.springerlink.com/doi:10.1007/s10096-005-0008-8
189. Kola, A., F. Mattner, U. Reischl, R.-P. Vornberg, K. Weist, C. Wendt, W. Witte, S. Ziesing, S. Suerbaum, and P. Gastmeier (2005) Workshop zum MRSA Screening in Hannover. Mikrobiologe 15:175-180.
190. Apfalter, P., U. Reischl, and M.R. Hammerschlag (2005) In-house nucleic acid amplification assays in research: how much quality control is needed before one can rely upon the results ?. J. Clin Microbiol. 43:5835-4041.
> http://jcm.asm.org/cgi/reprint/43/12/5835.pdf
191. Gastmeier, P., W. Witte, A. Kola, F. Mattner, R.-P. Vornberg, S. Ziesing, S. Ziesing, S. Suerbaum, U. Reischl, K. Weist, and C. Wendt (2005) Workshop der DGHM zu Methoden des MRSA-Screenings. Epidemiol. Bull. 42:2385-389.
> http://www.rki.de/cln_042/2005
192. Reischl, U., N. Lehn, H. Wolf, and E. Straube (2005) "Bakteriengenom-Nachweis PCR / NAT": Auswertung des aktuellen Ringversuchs von INSTAND e.V. zur externen Qualitätskontrolle molekularbiologischer Nachweisverfahren in der bakteriologischen Diagnostik. Mikrobiologe 15:50-59.
193. Reischl, U., N. Lehn, H. Wolf, and E. Straube (2005) "Bakteriengenom-Nachweis PCR / NAT": Auswertung des aktuellen Ringversuchs von INSTAND e.V. zur externen Qualitätskontrolle molekularbiologischer Nachweisverfahren in der bakteriologischen Diagnostik. Mikrobiologe 15:143-153.
194. Nübel, U., W. Witte, U. Reischl, et al. (2006) Workshop der DGHM zu Methoden des MRSA-Screenings. Epidemiol. Bull. 6:47-51. > http://www.rki.de/cln_006/2006
195. Birkenmaier, C., U. Reischl, and B. Stübinger (2006) Sterile abscess: a surprise diagnosis ? Scand. J. Infect. Dis. 38:15-18.
> http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/00365540500372630
196. Reischl, U. (2006) Indikationen für die molekulare Diagnostik - Bakterien, Pilze und Eukaryonten. In: Leitfaden Molekulare Diagnostik. Grundlagen, Tipps und Tricks für die Praxis (Thiemann, F., P.M. Cullen, and H.-G. Klein, eds.). ISBN 3-527-31471-7, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, pp. 175-184.
197. Kola A, I.F. Chaberny, F. Mattner, U. Reischl, R.P. Vonberg, K. Weist, C. Wendt, W. Witte, S. Ziesing, S. Suerbaum, and P. Gastmeier (2006) Control of methicillin-resistant S. aureus by active surveillance: Results of a workshop held by the Deutsche Gesellschaft fur Hygiene und Mikrobiologie. Anaesthesist 55:778–783.
> http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00101-006-1016-5
198. Reischl, U., N. Lehn, H. Wolf, M. Maaß, and E. Straube (2006) "Bakteriengenom-Nachweis PCR / NAT": Auswertung des aktuellen Ringversuchs von INSTAND e.V. zur externen Qualitätskontrolle molekularbiologischer Nachweisverfahren in der bakteriologischen Diagnostik. Mikrobiologe 16:145-157.
199. Reischl, U., M.-B. Alberdi, M. Hoffmann, and M. Bollwein (2006) Quantitative detection of Legionella pneumophila in water samples: assay transfer to the LightCycler 480 real-time PCR system. Biochemica 4:13-15.
200. Reischl, U., H. Melzl, R.M. Kroppenstedt, T. Miethke, L. Naumann, A. Mariottini, G. Mazzarelli, and E. Tortoli (2006) Mycobacterium monacense sp. nov. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 56:2575-2578. > http://dx.doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.64527-0
201. Reischl, U. (2006) Melting of the ribosomal RNA gene reveals bacterial species identity: a step toward a new rapid test in clinical microbiology. Clin. Chem. 52:1985-1987.
> http://dx.doi.org/10.1373/clinchem.2006.076240
202. Wilson, D.A., U. Reischl, G.S. Hall, and G.W. Procop (2007) The use of partial 16S rDNA gene sequencing for the identification of Legionella pneumophila and non-pneumophila legionella. J. Clin. Microbiol. 45:257-258.
> http://jcm.asm.org/cgi/reprint/45/1/257.pdf
203. Reischl, U., M.J. Tuhony, G.S. Hall, G.W. Procop, N. Lehn, and H.-J. Linde (2007) Rapid detection of Panton-Valentine leukocidin (PVL)-positive Staphylococcus aureus by real-time PCR targeting the lukS-PV gene. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Inf. Dis. 26:131-135.
> http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s10096-007-0254-z
204. Multi-author chapter incl. U. Reischl (2007) Experts roundtable: Real-Time PCR and Microbiology. In: Real-Time PCR in Microbiology: From Diagnosis to Characterization. (Ian M. Mackay; Edt.), Horizon Scientific Press, Norwich, U.K., pp. 357-443. ISBN: 9787774575798
205. Ruiz, A.*, U. Reischl* (*equal contributors), S.H. Swerdlow, M. Hartke, B. Streubel, G. Procop, R.R. Tubbs, and J.R. Cook (2007) Extranodal marginal zone B-cell lymphomas of the ocular adnexa: multiparameter analysis of 34 cases including interphase molecular cytogenetics and PCR for Chlamydia psittaci. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 31:792-802.
> http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/01.pas.0000249445.28713.88
206. U. Reischl (2006) Real-time PCR in Diagnostic Microbiology - a review on 9 years of R&D in an academic environment. In: qPCR 2007 Proceedings, (Pfaffl, M.W., edt.), ISBN 13-978-3-00-020386-5, TUM Tech, Munich, pp.29.
207. Reischl, U., N. Lehn, H. Wolf, M. Maaß, and E. Straube (2007) "Bakteriengenom-Nachweis PCR / NAT": Auswertung des Ringversuchs September 2006 von INSTAND e.V. zur externen Qualitätskontrolle molekularbiologischer Nachweisverfahren in der bakteriologischen Diagnostik. Mikrobiologe 17:105-119.
208. Sahrbacher, U., L. Naumann, U. Reischl, J. Schölmerich, and T. Glück (2007) Reduced TH-1 cytokine release in an adult patient with chronic relapsing Mycobacterium malmoense infection. Infection 35:282-286. > http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s15010-007-4101-z
209. Lück, P.C., C. Ecker, U. Reischl, H.-J. Linde, and R.Stempka (2007) Culture-independent identification of the source of the infection by direct amplification and sequencing of Legionella pneumophila DNA from clinical specimen. J. Clin. Microbiol. 45:3143-3144. > http://jcm.asm.org/cgi/reprint/45/9/3143.pdf
210. Hogardt, M. A.M. Schreff, L. Naumann, U. Reischl, and A. Sing (2008) Mycobacterium monacense in a patient with a pulmonary tumor. Jpn. J. Infect. Dis.61:77-78.
http://www.nih.go.jp/JJID/61/77.pdf
211. Bastien, P., G. Procop, and U. Reischl (2008) Quantitative real-time PCR is not more sensitive than 'conventional' PCR. J. Clin. Microbiol. 46:1897-1900.
> http://jcm.asm.org/cgi/reprint/46/6/1897.pdf
212. Bürgers, R., W. Schneider-Brachert, U. Reischl, A. Behr, K.-A. Hiller, N. Lehn, G. Schmalz, and S. Ruhl (2008) Helicobacter pylori in human oral cavity and stomach. Eur. J. Oral Sci. 116:297-304. [IF=1,74]
http://www3.interscience.wiley.com/cgi-bin/fulltext/120749190/PDFSTART
213. Tomaso, H., D. Jacob, M. Eickhoff, H.C. Scholz, S. Al Dahouk, M.M. Kattar, U. Reischl, H. Plicka, J.S. Olsen, S. Nikkari, P. Matero, C. Beuret, A, Ciammaruconi, F. Lista, J.L. Gala, H. Broll, B. Appel, R.E. Sellek-Cano, M. del Carmen Ybarra de Villavicencio, M. Broekhuijsen, A. Indra, R. petersen and H. Neubauer. (2008) Preliminary validation of real-time PCR assays for the identification of Yersinia pestis. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 46:1239-1244. > http://dx.doi.org/10.1515/CCLM.2008.251
214. Reischl, U. and T. Holzmann (2008) Direct nucleic acid-based detection of MRSA in clinical specimens. J. Lab. Med. 32:253-265. http://dx.doi.org/10.1515/jlm.2008.034
215. Gerber, M., C. Walch, B. Löffler, K. Tischendorf, U. Reischl, and G. Ackermann (2008) Effect of sub-MIC concentrations of metronidazole, vancomycin, clindamycin and linezolid on toxin gene transcription and production in Clostridium difficile. J. Med. Microbiol. 57:776-789. > http://dx.doi.org/10.1099/jmm.0.47739-0
216. Reischl, U., N. Lehn, H. Wolf, M. Maaß, and E. Straube (2008) "Bakteriengenom-Nachweis PCR / NAT": Auswertung des Ringversuchs April 2007 von INSTAND e.V. zur externen Qualitätskontrolle molekularbiologischer Nachweisverfahren in der bakteriologischen Diagnostik. Mikrobiologe 18:76-90.
217. Seal, D., U. Reischl, A. Behr, C. Ferrer, J. Alió, R.J. Koerner, P. Barry, and ESCRS Endophthalmitis Study Group (2008) Laboratory diagnosis of endophthalmitis: Comparison of microbiology and molecular methods in the European Society of Cataract & Refractive Surgeons multicenter study and susceptibility testing. J. Cataract Refract. Surg. 34:1439-1450.
> http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jcrs.2008.05.043
218. Reischl, U., N. Lehn, H. Wolf, M. Maaß, and E. Straube (2008) "Bakteriengenom-Nachweis PCR / NAT": Auswertung des Ringversuchs April 2008 von INSTAND e.V. zur externen Qualitätskontrolle molekularbiologischer Nachweisverfahren in der bakteriologischen Diagnostik. Mikrobiologe 18:175-188.
219. Buergers, R., T. Cariaga, R. Mueller, M. Rosentritt, U. Reischl, G. Handel, and S. Hahnel (2009) Effects of aging on surface properties and adhesion of Streptococcus mutans on various fissure sealants. Clin. Oral Investig. 13:419-426.
> http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00784-009-0256-6
220. Reischl, U. (2008) Survey on commercial PCR test systems and in-house protocols for direct detection of MRSA from swab specimens. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 298:100. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmm.2008.08.001
221 Buergers, R., S. Hahnel, U. Reischl, R. Mueller, M. Rosentritt, G. Handel, and M. Behr (2009) Streptococcal adhesion to various luting systems and the role of mixing errors. Acta Odontol. Scand. 67:3,139-145.
> http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/00016350902729251
222. Hartinger, A., U. Reischl (2009) PCR-basierte MRSA-Schnelltests – Höchste Zeit. Trillium-Report 7: 42-47. ISSN 1614-1946.
223. Ludwig, E., U. Reischl, D. Janik, and W. Hermanns (2009) Granulomatous pneumonia caused by Mycobacterium genavense in a dwarf rabbit (Oryctolagus cuniculus). Vet. Pathol. 49:1000-1002. [Epub ahead of print].
http://dx.doi.org/10.1354/vp.08-VP-0190-L-BC )
224. Reischl, U., N. Lehn, H. Wolf, M. Maaß, and E. Straube (2009) "Bakteriengenom-Nachweis PCR / NAT": Auswertung des Ringversuchs November 2008 von INSTAND e.V. zur externen Qualitätskontrolle molekularbiologischer Nachweisverfahren in der bakteriologischen Diagnostik. Mikrobiologe 19:91-103.
225. Reischl, U., E. Straube, and M. Unemo (2009) The Swedish new variant of Chlamydia trachomatis (nvCT) remains undetected by many European laboratories as revealed in the recent PCR/NAT ring trial organized by INSTAND e.V., Germany. Euro Surveill. 2009;14(32):pii=19302. Available online.
http://www.eurosurveillance.org/ViewArticle.aspx?ArticleId=19302.
226. Panning, M., M. Eickmann, O. Landt, M. Monazahian, S. Ölschläger, S. Baumgarte, U. Reischl, J.J. Wenzel, H.H. Niller, S. Günther, B. Hollmann, D. Huzly, J.F. Drexler, A. Hellmer, S. Becker, B. Matz, A.M. Eis-Hübinger, and C. Drosten (2009) Detection of Influenza A(H1N1)v virus by real-time RT-PCR. Euro Surveill. 2009;14(36):pii=19329. Available online: http://www.eurosurveillance.org/ViewArticle.aspx?ArticleId=19329
227. Dierkes C, B. Ehrenstein, S. Siebig, H.-J. Linde, U. Reischl, and B. Salzberger (2009) Clinical impact of a commercially available multiplex PCR system for rapid detection of pathogens in patients with presumed sepsis. BMC Infectious Diseases 9:126.
> http://www.biomedcentral.com/1471-2334/9/126
228. Kern, M., S. Böhm, L. Deml, H. Wolf, U. Reischl, and H.H. Niller (2009) Inhibition of Legionella pneumophila PCR in respiratory samples: a quantitative approach. J. Microbiol. Meth. 79:189-193. > http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.mimet.2009.08.020
229. Melzl H, J.J. Wenzel, B. Kochanowski, K. Feierabend, B. Kreuzpaintner, E. Kreuzpaintner, A. Rohrhofer, S. Schreder-Meindl, H. Wollner, B. Salzberger, U. Reischl, W. Jilg, H. Wolf, and H.H. Niller (2009) First sequence-confirmed case of infection with the new influenza A(H1N1) strain in Germany. Euro Surveill. 2009;14(18):pii=19203.
Available online: http://www.eurosurveillance.org/ViewArticle.aspx?ArticleId=19203
230. Wenzel, J.J., H. Walch, M. Bollwein, H.H.Niller, W. Ankenbauer, R. Mauritz, H.-J. Höltke, H.M. Zepeda, H. Wolf, W. Jilg, and U. Reischl (2009) Rapid development of real-time RT-PCR assays for the detection of novel influenza A/H1N1/09 virus by using a library of prefabricated locked nucleic acid hydrolysis probes. Clin. Chem. 55:2218-2222.
> http://dx.doi.org/10.1373/clinchem.2009.136192
231. Reischl, U., H.-J. Linde, H. Wolf, M. Maaß, E. Straube, and E. Jacobs (2009) "Bakteriengenom-Nachweis PCR / NAT": Auswertung des Ringversuchs Mai 2009 von INSTAND e.V. zur externen Qualitätskontrolle molekularbiologischer Nachweisverfahren in der bakteriologischen Diagnostik. Mikrobiologe 19:177-191.
232. Reischl, U., J. Frick, S. Hörmansdorfer, H. Melzl, M. Bollwein, H.-J. Linde, K. Becker, R. Köck, C. Tuschak, U. Busch, and A. Sing (2009) Single-nucleotide polymorphism in the SCCmec-orfX junction distinguishes between livestock-associated MRSA CC398 and human epidemic MRSA strains. Euro Surveill. 2009;14(49):pii=19436.
Available online: http://www.eurosurveillance.org/ViewArticle.aspx?ArticleId=19436
233. Hoffmann, H., U. Reischl (2009) Infektionsdiagnostik: TB or not TB?. Trillium-Report 7: 198-199. ISSN 1614-1946.
234. Nagarajan, A., M.Ananthi, P. Krishnan, U. Haas, U. Reischl, P. Chandrasekaran, and H.-J. Linde (2010) Emergence of Panton-Valentine Leukocidin (PVL) among Community- and Hospital-associated Meticillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in Chennai, South India. J. Hosp. Infect. 76: 269-271.
> http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jhin.2009.12.018
235. Reischl, U., H.-J. Linde, H. Wolf, M. Maaß, E. Straube, and E. Jacobs (2010) "Bakteriengenom-Nachweis PCR / NAT": Auswertung des Ringversuchs November 2009 von INSTAND e.V. zur externen Qualitätskontrolle molekularbiologischer Nachweisverfahren in der bakteriologischen Diagnostik. Mikrobiologe 20:63-78.
236. Wenzel, J.J., M. Panning, K.L. Kaul, K. Mangold, P.A. Revell, R.A. Luna, H. Zepeda, L. Perea, J.A Vazquez-Perez, S. Young, B. Rodic-Polic, M. Eickmann, C. Drosten, W. Jilg, and U. Reischl (2010) Analytical Performance Determination and Clinical Validation of the Novel Roche Diagnostics RealTime ready Influenza A/H1N1 Detection Set. J. Clin. Microbiol. 48:3088-3094. > http://jcm.asm.org/cgi/reprint/48/9/3088
237. Hanses, F., T. Huetz, U. Reischl, B.P. Ehrenstein, H.-J. Linde, and B. Salzberger (2011) Lack of evidence for persistent colonization with community-acquired methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in a central European cohort. Clin. Microbiol. Infect., 17:466-468.
> http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-0691.2010.03325.x
238. Held, J., M. Koch, U. Reischl, T. Danner, and A. Serr (2011) Serum (13)-D-Glucan measurement as early indicator for Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia and evaluation of its prognostic value. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 17:595-602.
> http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-0691.2010.03318.x
239. Indra, A., M. Blaschitz, S. Kernbichler, U. Reischl, G. Wewalka, and F. Allerberger (2010) Mechanisms behind variation in the Clostridium difficile 16S 23S rRNA intergenic spacer region. J. Med. Microbiol. 59:1317-1323.
> http://dx.doi.org/10.1099/jmm.0.020792-0
240. Reischl, U., W. Schneider, M. Maaß, E. Straube, V. Fingerle, and E. Jacobs (2010) Bakteriengenom-Nachweis PCR / NAT": Auswertung des Ringversuchs April 2010 von INSTAND e.V. zur externen Qualitätskontrolle molekularbiologischer Nachweisverfahren in der bakteriologischen Diagnostik. Mikrobiologe 20:181-197.
241. Reischl, U. (2010) Result report on the QCMD 2010 Mycobacterium tuberculosis DNA (MTBDNA10) EQA programme. Quality Control for Molecular Diagnostics. October 2010 issue: pp.1-7
242. Reischl, U., and R.P.H. Schmitz (2011) In search of a new gold standard: molecular appoaches to improve early diagnosis of microbial-induced sepsis. Eur. Infect. Dis. 5:44–46. p-ISSN: 1755-1137
243. Kaevska M., I. Slana, P. Kralik, U. Reischl, J. Orosova, A. Holcikova, and I. Pavlik (2011) Mycobacterium avium subsp. hominissuis in neck lymph nodes of children and their environment examined by culture and triplex quantitative real-time PCR (2011). J. Clin. Microbiol. 49:167-172.
> http://dx.doi.org/10.1128/JCM.00802-10
244. Ludwig, E.*, U. Reischl* (*equal contributors), T. Holzmann, D. Janik, C. Gilch, and W. Hermanns (2011) Risk for Mycobacterium celatum infection from ferret [letter]. Emerg Infect Dis. [serial on the Internet] 2011 Mar [date cited].
> http://dx.doi.org/10.3201/eid1703.100969
245. U. Reischl, C. Drosten, W. Geißdörfer, U. Göbel, K.S. Hoffmann, H. Mauch, T. Meyer, A. Moter, L. von Müller, M. Panning, H.F. Rabenau, I. Reiter-Owona, A. Roth and M. Weitz (2011) MiQ 1: Nukleinsäure-Amplifikationstechniken (NAT), 3. Auflage, In: Mikrobiologisch-infektiologische Qualitätsstandards (MiQ) Qualitätsstandards in der mikrobiologisch-infektiologischen Diagnostik (A. Podbielski, M. Herrmann, E. Kniehl, H. Mauch, and H. Rüssmann , eds.), ISBN-13: 978-3-437-41535-7, Urban & Fischer, München, pp. 1-80.
http://shop.elsevier.de/content/miq-01--qualitaetsstandards-in-der-mikrobiologischen-diagnostik/1468372.html
246. Reischl, U., W. Schneider, M. Maaß, E. Straube, V. Fingerle, and E. Jacobs (2011) Bakteriengenom-Nachweis PCR / NAT": Auswertung des Ringversuchs November 2011 von INSTAND e.V. zur externen Qualitätskontrolle molekularbiologischer Nachweisverfahren in der bakteriologischen Diagnostik. Mikrobiologe 22:181-197.
247. Sing, A., A. Berger, W. Schneider-Brachert, T. Holzmann, and U. Reischl (2011) Rapid detection and molecular differentiation of toxigenic Corynebacterium diphtheriae and Corynebacterium ulcerans strains by LightCycler PCR. J. Clin. Microbiol. 49:2485-2489. > http://dx.doi.org/10.1128/JCM.00452-11
248. Karasi, J.-C., F. Dziezuk, L. Quennery, S. Förster, U. Reischl, G. Colucci, D. Schoener, C. Devaux, and J.-C. Schmit (2011) High correlation between the Roche COBAS AmpliPrep/COBAS TaqMan HIV-1, v2.0 and the Abbott m2000 RealTime HIV-1 assays for quantification of viral load in HIV-1 B and non-B subtypes. J. Clin. Virol. 52:181-186 > http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jcv.2011.07.002
249. Bialek, R., M. Bollwein, and U. Reischl (2011) Use of MagNA Pure 96 and LightCycler systems for high throughput testing of stool samples for enterohemorrhagic E. coli (EHEC) in an outbreak. Roche Diagnostics MagNA Pure System Application Note. 3: 1-7.
> I-Net Link
250. Reischl, U., A. Berger and A. Sing (2012) Rapid detection and molecular differentiation of toxigenic Corynebacterium diphtheriae and Corynebacterium ulcerans strains by LightCycler PCR. Chapter of the revised WHO Manual for the Diagnosis of Diphtheria. (submitted).
251. Shaheed V.O., A. Roth, N.A. Ismail, L. Erasmus, M. Ehlers, M. Kock, N. Paulse, H.M. Said, A.A Hoosen, and U. Reischl (2011) Analytical performance of the Roche LightCycler® Mycobacterium Detection kit for the diagnosis of clinically important mycobacterial species. PLoS One. 2011;6(9):e24789. Epub 2011 Sep 22.
> http://dx.doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0024789
252. Reischl, U. (2011) Result report on the QCMD 2011 Mycobacterium tuberculosis DNA EQAS programme (MTBDNA11). Quality Control for Molecular Diagnostics. November 2011 issue: pp.1-8.
253. Kirchgesser, M., A. Aschenbrenner, M. Bollwein, and U. Reischl (2011) High-throughput detection of bacterial, fungal and viral nucleic acids in routine microbiological sample types using one generic Pathogen Universal Protocol on the MagNA Pure 96 System. Roche Diagnostics MagNA Pure System Application Note. 5: 1-8.
> I-Net Link
254. Reischl, U., R. Enzensberger, B. Boeddinghaus, K.-P. Hunnfeld und J. Wenzel (2012) Kap. 42.12 Mykobakterien-Infektion. In: Labor und Diagnose: Indikation und Bewertung von Laborbefunden für die medizinische Diagnostik, 8. Aufl. (L. Thomas, edt.), ISBN-978-3-9805215-8-1, LH-Books Verlagsgesellschaft, Frankfurt, pp. 1994-2002.
255. Reischl, U. und H.F. Rabenau (2012) Die aktuelle MIQ-1 "Nukleinsäure-Amplifikationstechniken (PCR/NAT)" (3. Auflage) - was ist neu ?. Mikrobiologe 22:48-52.
256. Holzmann, T., D. Frangoulidis, M. Simon, P. Noll, S. Schmoldt, M. Hanczaruk, G. Grass, M. Pregler, A. Sing, S. Hörmansdorfer , H. Bernard, R. Grunow, R. Zimmermann, W. Schneider-Brachert, A. Gessner, and U. Reischl (2012) Fatal anthrax infection in a heroin user from southern Germany, June 2012. Euro Surveill. 2012;17(26):pii=20204.
Available online: http://www.eurosurveillance.org/ViewArticle.aspx?ArticleId=20204
257. Fieser, N., U. Simnacher, Y. Tausch, S. Belak, S. Ladenburger-Strauß, H. von Baum, U. Reischl, and A. Essig (2013) Chlamydia trachomatis Prevalence, Genotype Distribution and Sporadic Emergence of the New Swedish Variant in Southern Germany. Infection 41:159-166. > http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s15010-012-0301-2
258. Hanczaruk, M., U. Reischl, T. Holzmann, D. Frangoulidis, D.M. Wagner, P.S. Keim, M.H. Antwerpen, H. Meyer and G. Grass (2014) Injectional anthrax in heroin users, Europe, 2000–2012. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 20:322-323.
> http://dx.doi.org/10.3201/eid2002.120921
259. Rückert C., K. Licht, J. Kalinowski, C.E. Santo, M. Antwerpen, M. Hanczaruk, U. Reischl, T. Holzmann, A. Gessner, C. Tiemann, and G. Grass (2012) Draft genome sequence of Bacillus anthracis UR-1 isolated from a German heroin user. J. Bacteriol. 194:5997-5998. > http://dx.doi.org/10.1128/JB.01410-12
260. Reischl, U., W. Schneider, M. Maaß, E. Straube, V. Fingerle, and E. Jacobs (2012) Bakteriengenom-Nachweis PCR / NAT": Auswertung des Ringversuchs Mai 2012 von INSTAND e.V. zur externen Qualitätskontrolle molekularbiologischer Nachweisverfahren in der bakteriologischen Diagnostik. Mikrobiologe 23:53-67.
261. Salzberger, B., K. Becker, H. Fickenscher, A. Gessner, T. Holzmann, W. Kern, F. Mattner, A. Niederbichler, S. Suerbaum, U. Reischl (2012) Positionspapier der Deutschen Gesellschaft für Infektiologie (DGI) und der Deutschen Gesellschaft für Hygiene und Mikrobiologie (DGHM) zu Injektions-Anthrax (Milzbrand). pp.1-8.
> http://www.dgi-net.de/Injektions-Anthrax_2012
262. Grunow, R., L. Verbeek, D. Jacob, T. Holzmann, G. Birkenfeld, D. Wiens, L. von Eichel-Streiber, G. Grass, and U. Reischl (2012) Injection anthrax - a new outbreak in heroin users. Dtsch. Ärztebl. Int. 109:843-848.
> http://dx.doi.org/10.3238/arztebl.2012.0843
263. Hanczaruk, M., U. Reischl, T. Holzmann, and G. Grass (2012) Informationen zu Milzbrandinfektionen bei Heroinkonsumenten - Information on anthrax infections in heroin users. Wehrmed. Mschr. 56: 260-262.
> http://www.wehrmed.de/article/2178
264. Reischl, U., O. Landt, H.F. Rabenau and W. Geissdörfer (2012) Nukleinsäurediagnostik im mikrobiologischen Labor - Neue Möglichkeiten des kulturunabhängigen Erregernachweises, der Speziesdifferenzierung und molekularen Resistenztestung. 1. Aufl. (U. Reischl, edt.), ISBN 978-3-8374-2254-2, Uni-Med Verlag, Bremen, pp. 1-137.
265. Becker, K., H. Fickenscher, A. Gessner, T. Holzmann, W. Kern, F. Mattner, A. Niederbichler, S. Suerbaum, U. Reischl, B. Ruf, B. Salzberger, and S. Suerbaum (2013) Positionspapier der Deutschen Gesellschaft für Infektiologie (DGI) und der Deutschen Gesellschaft für Hygiene und Mikrobiologie (DGHM) zu Injektions-Anthrax (Milzbrand). Mikrobiologe 23:68-72.
266. Hiergeist, A. and U. Reischl, (2013) Stellenwert der PCR in der Infektionsdiagnostik., Sektion: Labor & Diagnostik, Management & Krankenhaus 3:27.
267. Reischl, U., (2013) Nukleinsäurediagnostik im mikrobiologischen Labor - Wunderbarer Wildwuchs". Trillium Diagnostik 11: 16-18. ISSN 1614-1946.
268. Reischl, U., E. Straube, M. Maaß, E. Jacobs, W. Schneider, V. Fingerle, U. Busch, D. Frangoulidis, W. Splettstösser, G. Grass, and I. Reiter-Owona (2012) Bacterial and fungal genome detection PCR/NAT: discussion of the May 2013 distribution for external quality assessment of nucleic acid-based protocols in diagnostic medical microbiology by INSTAND e.V. GMS Z. Forder. Qualitatssich. Med. Lab. 2013;4:Doc03 ISSN 1869-4241
> http://dx.doi.org/10.3205/lab000010
269. Schmidt, D., H. Päschke, V. Bremer, O. Hamouda, U. Reischl, A. Sailer and K. Haar (2014) An assessment of current Chlamydia trachomatis laboratory practices in Germany. Gesundheitswesen, 75:7-18.
> http://dx.doi.org/10.1055/s-0033-1355406
270. Moter, A., D. Schmiedel, A. Petrich, A. Wiessner, J. Kikhney, T. Schneider, V. Moos, U.B. Göbel, and U. Reischl (2013) Validation of an rpoB gene PCR assay for detection of Tropheryma whipplei: 10 years' experience in a national reference laboratory. J. Clin. Microbiol. 51:3858-3861.
> http://dx.doi.org/10.1128/JCM.01703-13
271. Reischl, U., W. Schneider, M. Maaß, E. Straube, V. Fingerle, A. Sing, E. Jacobs, and I. Reiter-Owona (2013) Bakteriengenom-Nachweis PCR / NAT": Auswertung des Ringversuchs Mai 2013 von INSTAND e.V. zur externen Qualitätskontrolle molekularbiologischer Nachweisverfahren in der bakteriologischen Diagnostik. Mikrobiologe 23:172-188.
272. Reischl, U., W. Schneider, T. Holzmann, M. Ehrenschwender, M. Maaß, E. Straube, D. Frangoulidis, G. Grass, W. Splettstösser, V. Fingerle, A. Sing, E. Jacobs, and I. Reiter-Owona (2014) Bacterial and fungal genome detection PCR/NAT: discussion of the November 2013 distribution for external quality assessment of nucleic acid-based protocols in diagnostic medical microbiology by INSTAND e.V. . GMS Z. Forder. Qualitatssich. Med. Lab. 2014; 5:Doc01. ISSN 1869-4241
> http://dx.doi.org/10.3205/lab000011